There seems to be a direct relationship between how lifelike humanoid robots have evolved and their capacity to scare a real person out.
An sophisticated humanoid robot awakens from what looks to be a deep sleep in one video. Its remarkably human-like face, despite a gray pallor, displays realistic surprise at seeing its own hand and much more amazement when it discovers it is being videotaped. It doesn’t take long for the humanoid to reach out and shake hands with a welcoming grin, despite first seeming unnerved by both its own existence and the existence of the people around.
On the other hand, humans are unlikely to swiftly get over their own trepidation—and for some, plain fear—of humanoid robots. Masahiro Mori, a roboticist, created the term “the uncanny valley” to characterize the effect of realistic-looking robots on people’s comfort levels more than 50 years ago.
Why Do Humanoid Robots Exist?
Robots that resemble people and behave like them are called humanoid robots. These robots are frequently equipped with a variety of cameras, sensors, and, more recently, AI and machine learning technologies. They are typically designed to mimic real human expressions, interactions, and movements.
But any initial unease may soon fade as more humanoid robots are introduced into the world and have a positive impact in sectors like logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, and hospitality.
What Applications Do Humanoid Robots Have Today?
Despite the fact that many humanoid robots are still in the prototype or other early phases of development, others have eluded research and development in recent years and are now employed as bartenders, concierges, deep-sea divers, and elderly people’s companions. Some people support those in logistics and production by working in warehouses and factories. Others lead orchestras and welcome attendees to conferences, which appear to provide more novelty and amazement than anything else.
Although there are few humanoid robots in use today and their development is expensive, the market is predicted to expand. According to research company MarketsandMarkets, the market for humanoid robots is expected to be worth $1.8 billion in 2023 and more than $13 billion during the following five years. Advanced humanoid robots with enhanced AI capabilities and human-like qualities that can do more tasks in the service sector, in education, and in healthcare will fuel that development and demand.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk informed an audience at Tesla AI Day in 2021 that the company’s humanoid robot, Optimus, will be able to do “dangerous, repetitive, and boring tasks” like grocery shopping. In 2022, Tesla published a teaser photograph of a prototype of Optimus. The robot Optimus, which can do simple tasks and move slowly, is still being produced as of 2023. Additionally, Musk forecasted that the market value of his company’s humanoid robot segment will eventually surpass that of his electric car sector.
What Use Are Made Of Humanoid Robots?
In Spain, self-contained kiosks employ humanoid robots like Kime to pour and serve customers’ beverages and food. Some of them even hold jobs that require them to interact with customers, like hotel concierges.
Robotic humanoids in education In educational contexts, Nao and Pepper collaborate with students to develop material and instruct programming.
Other humanoid robots are already working in the healthcare industry, talking with patients and taking vital signs.
However, pilot studies examining their capability to safely operate and interact with human counterparts on factory floors, warehouses, and other locations will need to be completed before businesses can completely release their humanoid robots.
Uncertainty exists on how well humanoids will fit into society and how well people will accept their assistance. While some may view the widespread use of these robots as unsettling, hazardous, or as unnecessary competition in the labor market, the advantages, such as enhanced productivity and safety, may exceed many of the perceived negative effects.
In either case, humanoid robots are expected to have a significant influence; thankfully, we already have some of them around us that we can learn from. Here are a handful of the best humanoid robots now operating in our globe.
1 AMECA (ENGINEERED ARTS)
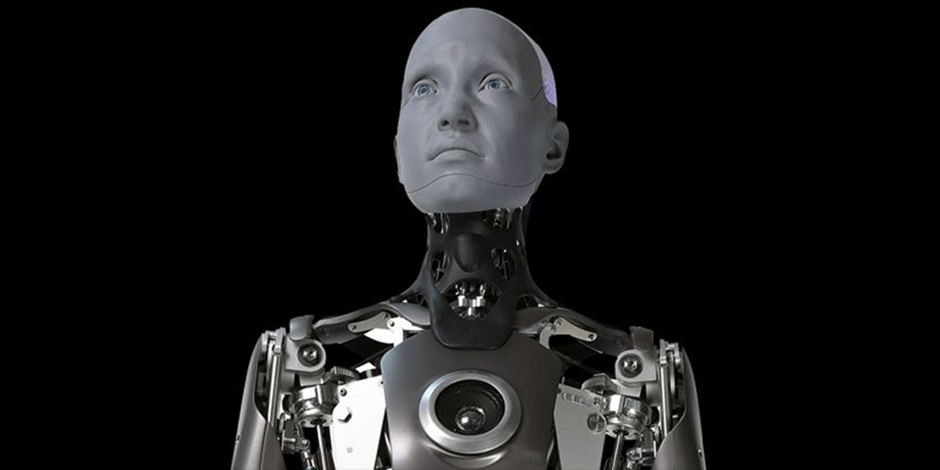
Ameca, the newest and most sophisticated humanoid robot from Engineered Arts, is marketed as a testing ground for AI and machine learning systems. Ameca communicates with people in a natural way and can recognize emotions and age thanks to sensors that can monitor movement around a space and face and various voice recognition capabilities. Ameca is capable of expressing typical emotions like amazement and surprise, as well as actions like yawning and shrugging.
2 ARMAR-6 (KARLSRUHE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY)
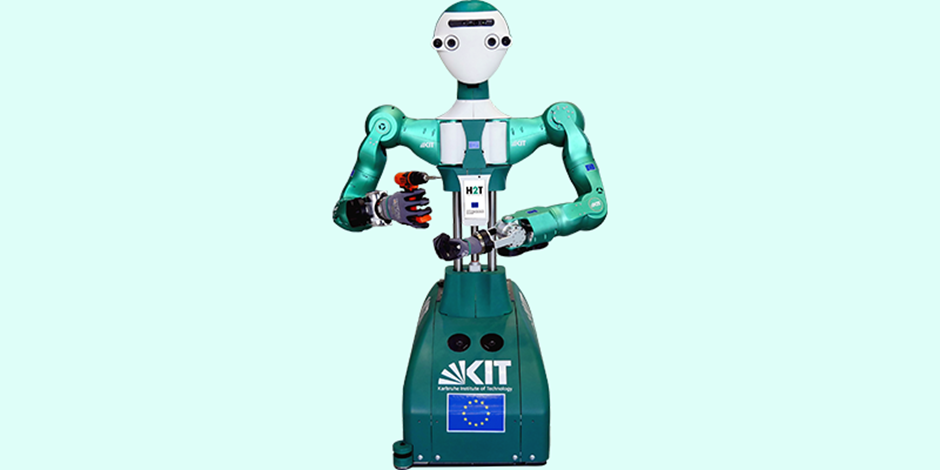

Researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany created the humanoid robot ARMAR-6 to operate in industrial environments. In addition to having the ability to use drills, hammers, and other tools, ARMAR-6 has AI technology that teaches it how to grip items and give them to human coworkers. Additionally, it is capable of doing maintenance tasks like cleaning off surfaces and may even request assistance when necessary.
3 APOLLO (APPTRONIK)
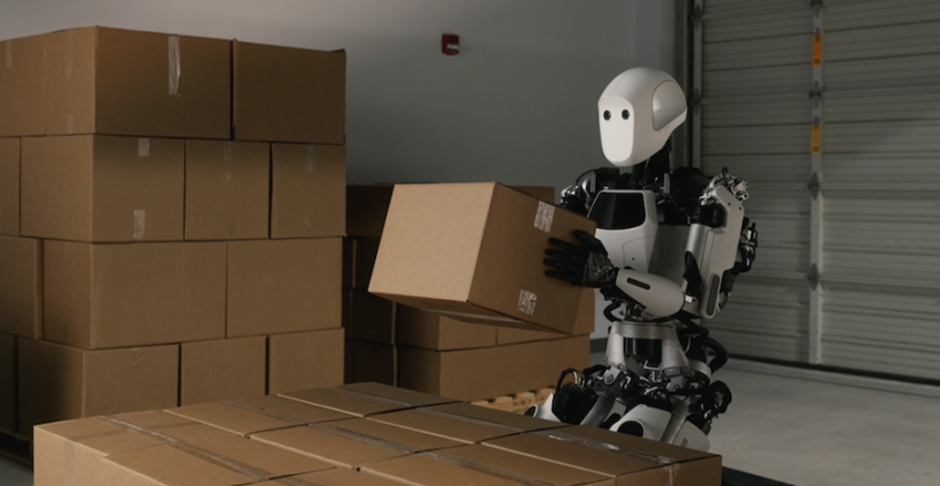

Apollo is the outcome of Apptronik expanding on its prior robots’ learnings, especially the humanoid robot Astro from 2022. Apollo, with a carrying capacity of up to 55 pounds, is intended to operate in warehouses and factories, with the potential to extend into sectors including construction and retail. The robot has an impact zone that enables it to halt its movement when it notices adjacent moving things, and Apollo is powered by interchangeable batteries that last for four hours apiece.
4 ATLAS (BOSTON DYNAMICS)

Boston Dynamics created the jumping, backflipping Atlas humanoid robot, which makes use of depth sensors for real-time perception and model-predictive control technologies for better mobility. Atlas stands 5 feet tall, weighs 196 pounds, has 28 hydraulic joints, three onboard computers, and travels at more than 5 miles per hour. Company roboticists employ Atlas, which was constructed using 3D-printed components, as a research and design tool to improve human-like agility and coordination.
5 BEOMNI (BEYOND IMAGINATION)

The humanoid robot Beomni, developed by Beyond Imagination, is operated remotely by “human pilots” wearing virtual reality headsets and other wearable equipment like gloves, while AI aids in Beomni’s task learning so that it can eventually be self-sufficient. In 2022, Harry Kloor, the CEO and co-founder of Beyond Imagination, told Built In that he was optimistic that Beomni will revolutionize the care that elderly people receive while taking over more risky and arduous employment in other sectors. Additionally, the business pledged to provide SELF Labs 1,000 humanoid robots over the course of five years as part of a farm simulation game.
6 DIGIT (AGILITY ROBOTICS)

Digit, a humanoid robot from Agility Robotics, can already move goods and unload trucks, and he’s ready to tackle even more laborious jobs. With completely functional limbs, Digit can pick up things by crouching and squatting, altering its center of gravity based on size and weight, and using surface plane-reading sensors to locate the quickest route to go around any obstacles. To test autonomous package delivery in 2019, Agility teamed up with Ford, and in 2022, the business raised $150 million from Amazon and other businesses to support Digit’s entry into the workforce.
7 NAO (SOFTBANK ROBOTICS)
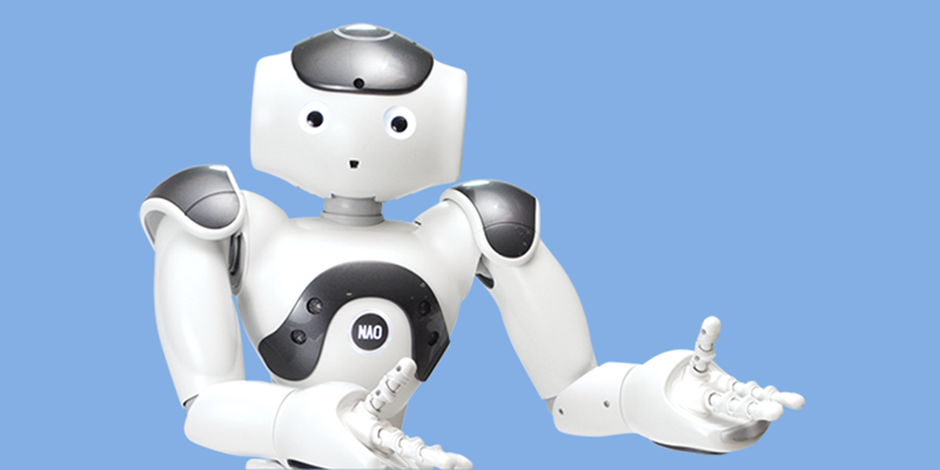
NAO, the first humanoid robot from Softbank Robotics, serves as a helper for businesses and institutions in sectors ranging from healthcare to education. NAO, a robot that stands just 2 feet tall, has two 2D cameras for object identification, four directional microphones and speakers, seven touch sensors, and other characteristics that help it interact with humans and its surroundings. NAO is assisting in content creation, teaching programming in classrooms, acting as assistants and patient service reps in hospital environments, and speaking and conversing in 20 different languages.
8 OCEANONE (STANFORD ROBOTICS LAB)
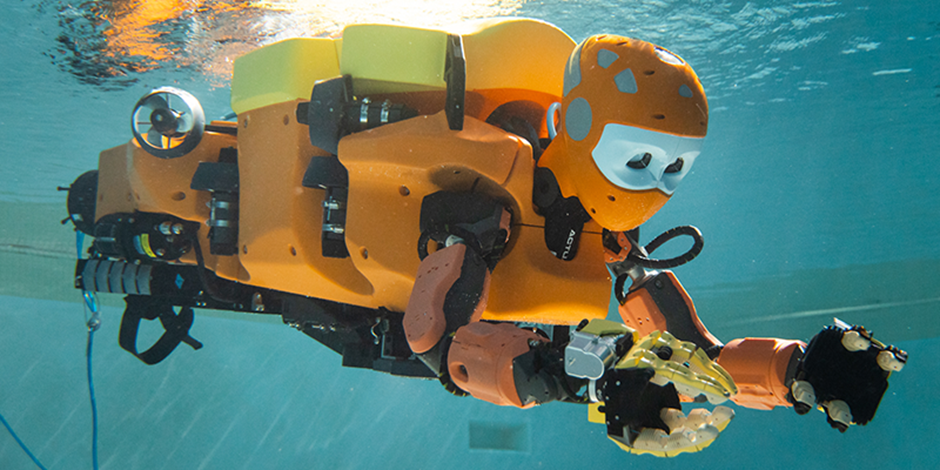

OceanOne, a humanoid diving robot from the Stanford Robotics Lab, is investigating shipwrecks. OceanOne set off in 2016 on its inaugural expedition to the Mediterranean Sea off the French coast to investigate the La Lune disaster, one of King Louis XIV’s ships that was wrecked in 1664. The humanoid robot developed by Stanford is capable of diving to a depth of 1,000 meters in its most recent incarnation, called OceanOneK. OceanOneK can control tools and other equipment and has previously examined underwater plane and ship wreckages. It also provides haptic feedback.



